贪心算法 动态规划:每次选取最大值:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public int wiggleMaxLength (int [] nums) {if (nums.length == 1 ) return 1 ;int lastNum = 0 ;0 ];int k = 1 ;boolean flag;boolean newflag;int [] dp = new int [nums.length];0 ] = 1 ;while (k < nums.length && nums[k] == nums[0 ]) {1 ;if (k == nums.length) return 1 ;2 ;true : false ;for (int i = k + 1 ; i < dp.length; i++) {if (nums[i] == lastNum) {1 ];else {true : false ;if (newflag == flag) {1 ];else {1 ] + 1 ;return dp[nums.length - 1 ];
来点更简洁的dp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public int wiggleMaxLength (int [] nums) { int [][] dp = new int [nums.length][2 ];0 ][0 ] = 1 ;0 ][1 ] = 1 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {0 ] = 1 ;1 ] = 1 ;for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) {if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {0 ] = Math.max(dp[i][0 ], dp[j][1 ] + 1 );else if (nums[i] < nums[j]) {1 ] = Math.max(dp[i][1 ], dp[j][0 ] + 1 );return Math.max(dp[nums.length - 1 ][0 ], dp[nums.length - 1 ][1 ]);
能用dynamic programming尽量不用贪心算法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public int jump (int [] nums) {int max = 0 ;int [] dp = new int [nums.length];0 ] = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i <= max; i++) {int newMax = Math.max(nums[i] + i, max);if (newMax > max) {for (int j = max + 1 ; j <= newMax && j < nums.length; j++) {1 ;if (max >= nums.length - 1 ) break ;return dp[nums.length - 1 ];
回溯算法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>();private LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>();public List<List<Integer>> combine (int n, int k) {1 );return result;private void backtracking (int n, int k, int startindex) {if (path.size() == k) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;for (int i = startindex; i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1 ; i++) {1 );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>();private LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3 (int k, int n) {1 , 0 );return result;private void backtracking (int k, int target, int startindex, int sum) {if (sum > target) return ;if (path.size() == k) {if (target == sum) result.add(new ArrayList <>(path));return ;for (int i = startindex; i <= 9 ; i++) {1 , sum);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 private List<String> result = new ArrayList <>();private StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder ();private HashMap<Integer, String> hp = new HashMap <>();public List<String> letterCombinations (String digits) {if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0 ) {return result;2 , "abc" );3 , "def" );4 , "ghi" );5 , "jkl" );6 , "mno" );7 , "pqrs" );8 , "tuv" );9 , "wxyz" );return result;private void backtracking (String digits) {if ("" .equals(digits)) {return ;int i = digits.charAt(0 ) - '0' ;String s = hp.get(i);for (int j = 0 ; j < s.length(); j++) {1 , digits.length()));1 );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>();private LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) {0 , 0 );return result;private void backtracking (int [] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex) {if (sum > target) return ;if (sum == target) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
这里需要考虑到提前清除重复选择,而且重复选择是在树的同层被清除的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>();private LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2 (int [] candidates, int target) {boolean [] used = new boolean [candidates.length];0 , 0 , used);return result;private void backtracking (int [] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex, boolean [] used) {if (target == sum) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++) {if (i >= 1 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1 ] && used[i - 1 ] == false ) continue ;true ;1 , used);false ;
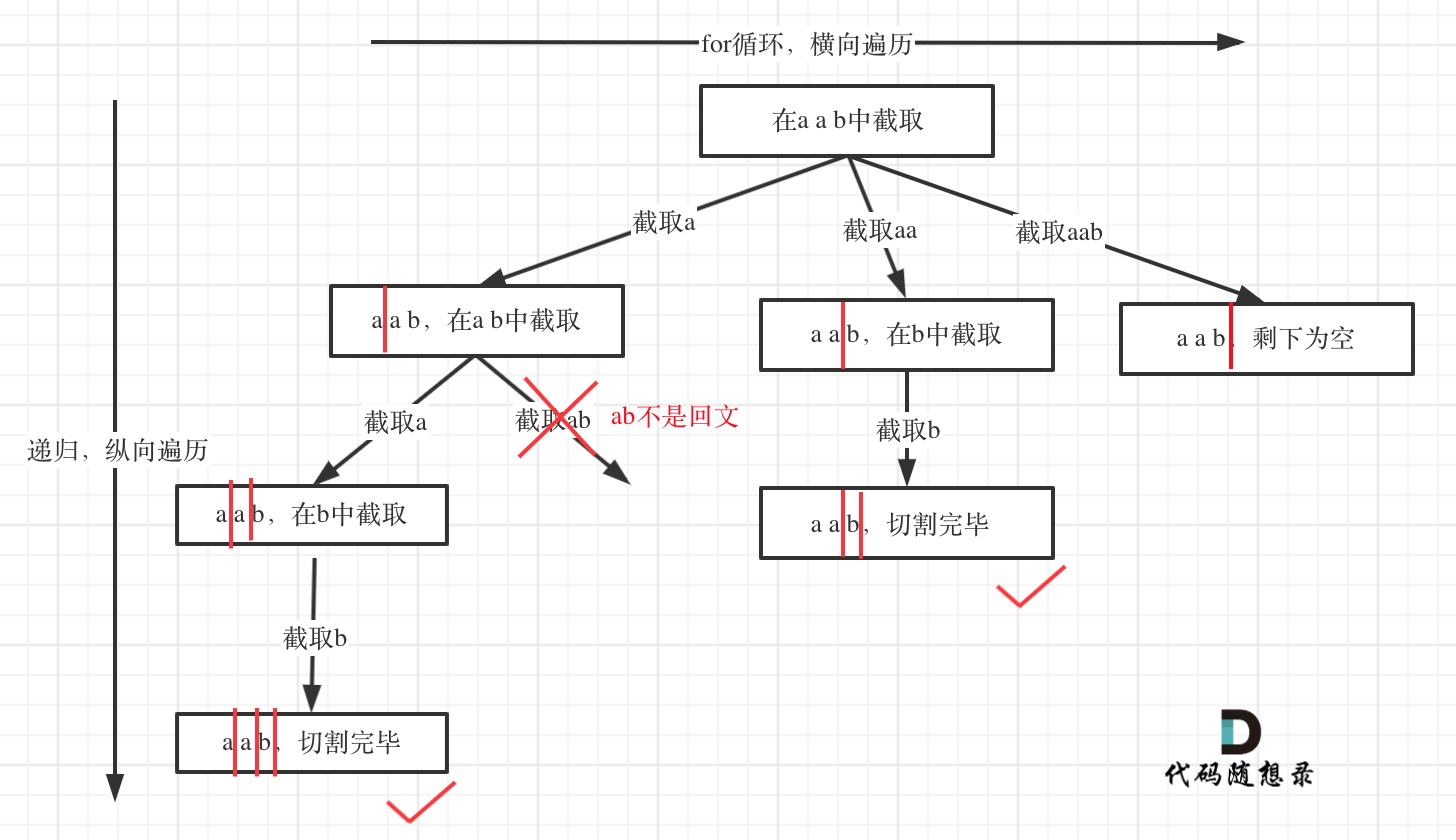
对于这个树形结构 for循环是同一次切割
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 private List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList <>();private LinkedList<String> path = new LinkedList <>();public List<List<String>> partition (String s) {0 );return result;private void backtracking (String s, int startIndex) {if (startIndex >= s.length()) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {if (isPalindrome(s.substring(startIndex, i + 1 ))) {1 ));else {continue ;1 );private boolean isPalindrome (String str) {for (int i = 0 , j = str.length() - 1 ; i < j; i++, j--) {if (str.charAt(i) != str.charAt(j)) return false ;return true ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 private List<String> result = new ArrayList <>();private LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>();public List<String> restoreIpAddresses (String s) {if (s.length() > 12 && s.length() < 4 ) return result;0 );return result;private void backtracking (String s, int startIndex) {if (path.size() == 3 ) {String s1 = s.substring(startIndex, s.length());if (s1.length() > 1 && s1.charAt(0 ) == '0' || s1.length() == 0 || s1.length() > 3 ) {return ;Integer i = Integer.parseInt(s1);if (i > 255 ) return ;StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder ();for (Integer integer : path) {"." );1 , sb.length());return ;for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {String s1 = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1 );if (s1.length() > 1 && s1.charAt(0 ) == '0' || s1.length() == 0 || s1.length() > 3 ) {break ;if (Integer.parseInt(s1) > 255 ) break ;1 );
在LeetCode78的基础上,增加了去重的操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>();private LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>();public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup (int [] nums) {boolean [] used = new boolean [nums.length];0 , used);return result;private void backtracking (int [] nums, int startIndex, boolean [] used) {new ArrayList <>(path));if (startIndex >= nums.length) {return ;for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {if ( i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ] && used[i - 1 ] == false ) {continue ;true ;1 , used);false ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>();private LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>();public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences (int [] nums) {0 );return result;private void backtracking (int [] nums, int startIndex) {if (path.size() >= 2 ) result.add(new ArrayList <>(path));new HashSet <>();for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {if (path.size() > 0 && nums[i] < path.getLast() || hs.contains(nums[i])) {continue ;1 );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>();private LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>();private HashSet<Integer> hs = new HashSet <>();public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique (int [] nums) {0 );return result;private void backtracking (int [] nums, int startIndex) {if (path.size() == nums.length) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;new HashSet <>();for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {if (hs.contains(i) || ht.contains(nums[i])) {continue ;
不使用set,改为使用used数组处理,速度更快:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>();private LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>();public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique (int [] nums) {boolean [] used = new boolean [nums.length];return result;private void backtracking (int [] nums, boolean [] used) {if (path.size() == nums.length) {new ArrayList <>(path));return ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {if (used[i] == true || i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ] && used[i - 1 ] == false ) continue ;true ;false ;
总的来说,在同一层数量去重就是在循环内部处理,在同一树枝去重就是在递归函数这一级别处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 private List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList <>();public List<List<String>> solveNQueens (int n) {char [][] chessboard = new char [n][n];for (char [] c : chessboard) {'.' );0 , chessboard);return result;private void backtracking (int n, int row, char [][] chessboard) {if (row == n) {return ;for (int col = 0 ; col < n; col++) {if (isValid(row, col, n, chessboard)) {'Q' ;1 , chessboard);'.' ;private boolean isValid (int row, int col, int n, char [][] chessboard) {for (int i = 0 ; i < row; i++) {if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q' ) return false ;for (int i = row - 1 , j = col - 1 ; i >= 0 && j >= 0 ; i--, j--) {if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q' ) {return false ;for (int i = row - 1 , j = col + 1 ; i >= 0 && j <= n - 1 ; i--, j++) {if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q' ) {return false ;return true ;private List<String> Array2List (char [][] chessboard) {new ArrayList <>();for (char [] c : chessboard) {return list;
回溯算法总结 回溯算法能解决如下问题:
组合问题:N个数里面按一定规则找出k个数的集合
排列问题:N个数按一定规则全排列,有几种排列方式
切割问题:一个字符串按一定规则有几种切割方式
子集问题:一个N个数的集合里有多少符合条件的子集
棋盘问题:N皇后,解数独等等
组合问题 for循环横向遍历,递归纵向遍历,回溯不断调整结果集
切割问题 同组合问题解决,如果想到了用求解组合问题的思路来解决 切割问题本题就成功一大半。
子集问题 注意去重方式,用hash表还是used数组。
棋盘问题 N皇后问题。
栈和队列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class MyQueue {private Stack<Integer> stackIn;private Stack<Integer> stackOut;public MyQueue () {new Stack <>();new Stack <>();public void push (int x) {public int pop () {if (stackOut.isEmpty()) {while (!stackIn.isEmpty()) {return stackOut.pop();else {return stackOut.pop();public int peek () {if (stackOut.isEmpty()) {while (!stackIn.isEmpty()) {return stackOut.peek();else {return stackOut.peek();public boolean empty () {return stackOut.isEmpty() && stackIn.isEmpty();
双队列法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class MyStack {private Queue<Integer> queueIn;private Queue<Integer> queueData;public MyStack () {new LinkedList <>();new LinkedList <>();public void push (int x) {while (!queueIn.isEmpty()) {while (!queueData.isEmpty()) {public int pop () {return queueIn.poll();public int top () {return queueIn.peek();public boolean empty () {return queueIn.isEmpty();
单队列法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class MyStack {private Queue<Integer> queue;public MyStack () {new LinkedList <>();public void push (int x) {int size = queue.size();while (size > 0 ) {public int pop () {return queue.poll();public int top () {return queue.peek();public boolean empty () {return queue.isEmpty();
优先级队列:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public int [] topKFrequent(int [] nums, int k) {int []> pq = new PriorityQueue <>((o1, o2)-> o1[1 ] - o2[1 ]);new HashMap <>();int [] result = new int [k];for (int num : nums) {if (hp.containsKey(num)) {1 );else {1 );for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : hp.entrySet()) {int [] tmp = new int [2 ];0 ] = entry.getKey();1 ] = entry.getValue();if (pq.size() > k) {for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) {0 ];return result;
此题核心在于构造单调队列,保障从单调队列中peek的元素是最大值,对于offer操作,若入口有更小的,全部remove,对于poll,只有移除的值与peek相同,才poll掉。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class Solution {public int [] maxSlidingWindow(int [] nums, int k) {MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue ();int [] result = new int [nums.length - k + 1 ];int i = 1 , j = k;for (int l = 0 ; l < k; l++) {0 ] = myQueue.peek();for (; j < nums.length; i++, j++) {1 ]);return result;class MyQueue {public MyQueue () {new LinkedList <>();void poll (int val) {if (!deque.isEmpty() && val == deque.peek()) {void offer (int val) {while (!deque.isEmpty() && val > deque.getLast()) {int peek () {return deque.peek();
单调栈 单调栈原始写法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public int [] dailyTemperatures(int [] temperatures) {int [] resuls = new int [temperatures.length];new Stack <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < temperatures.length; i++) {if (stack.isEmpty()) {else {if (temperatures[i] <= temperatures[stack.peek()]) {else {while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]) {Integer pop = stack.pop();return resuls;
单调栈简化写法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public int [] dailyTemperatures(int [] temperatures) {int [] resuls = new int [temperatures.length];new Stack <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < temperatures.length; i++) {while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]) {Integer pop = stack.pop();return resuls;
遍历两遍:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public int [] nextGreaterElements(int [] nums) {new Stack <>();int [] result = new int [nums.length];for (int i = 0 ; i < result.length; i++) {1 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums[i] > nums[stack.peek()]) {int max = nums[0 ], index = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) {if (nums[i] > max) {for (int i = index + 1 ;(i - nums.length) <= index; i++) {while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums[i % nums.length] > nums[stack.peek()]) {return result;
简化一下: 直接遍历长度* 2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public int [] nextGreaterElements(int [] nums) {new Stack <>();int [] result = new int [nums.length];for (int i = 0 ; i < result.length; i++) {1 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length * 2 ; i++) {while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums[i % nums.length] > nums[stack.peek()]) {return result;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public int trap (int [] height) {new Stack <>();int area = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < height.length; i++) {while (!stack.isEmpty() && height[i] > height[stack.peek()]) {int rightHeight = height[i];int nowHeight = height[stack.pop()];int leftHeight = 0 ;if (!stack.isEmpty()) {else {continue ;int realHeight = Math.min(rightHeight, leftHeight) - nowHeight;int width = i - stack.peek() - 1 ;return area;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public int largestRectangleArea (int [] heights) {int [] newheights = new int [heights.length + 2 ];for (int i = 0 ; i < heights.length; i++) {1 ] = heights[i];new Stack <>();int maxArea = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < newheights.length; i++) {while (!stack.isEmpty() && newheights[i] < newheights[stack.peek()]) {int rightIndex = i;int height = newheights[stack.pop()];int leftIndex = stack.peek();1 ));return maxArea;